江苏齐氏生物科技有限公司品牌商
16 年
手机商铺
- NaN
- 0.2999999999999998
- 0.2999999999999998
- 2.3
- 2.3
推荐产品
公司新闻/正文
贺复旦大学附属中山医院应用CHI Scientific产品成功发表SCI论文(IF:4.21)
1183 人阅读发布时间:2015-02-03 15:29
贺复旦大学附属中山医院应用CHI Scientific产品成功发表SCI论文(IF:4.21)
human primary dermal vascular smooth muscle cells, CHI Scientific
Arthritis Research & Therapy 2014, 16:4223 DOI:10.1186/s13075-014-0512-2 Published: 31 December 2014
Mengguo Liu1 , Ji Yang1, Xiaojing Xing1, Xiangxiang Cui1, Ming Li1
1Department of Dermatology, Zhongshan Hospital, Fudan University, 180 Fenglin Road, Shanghai 200032, China
Abstract
Introduction
Dermal vascular smooth muscle cells (DVSMCs) are important for vascular wall fibrosis in microangiopathy of systemic sclerosis (SSc). T helper 17 cells-associated cytokines, particularly interleukin-17A (IL-17A), have been demonstrated to play a role in the pathogenesis of SSc. However, the effect of IL-17A on the DVSMCs in microangiopathy of SSc has not been established. In the present study, we investigated the effect of IL-17A on the SSc patient-derived DVSMCs.
Methods
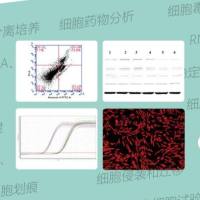
DVSMCs from patients with SSc and healthy subjects were incubated using IL-17A or serum derived from patients with SSc. Subsequently, the proliferation, collagen synthesis and secretion, and migration of DVSMCs were analysed using a cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8), dual luciferase reporter assay, real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR), western blot, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and transwell assay. The protein phosphorylation of signalling pathways in the process of IL-17A-mediated DVSMC activation was investigated and validated by specific signalling pathway inhibitor.
Results
IL-17A and serum from patients with SSc could promote the proliferation, collagen synthesis and secretion, and migration of DVSMCs. IL-17A neutralising antibody could inhibit the IL- 17A-induced activation of DVSMCs. Additionally, IL-17A induced the activation of extracellular regulated protein kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) in DVSMCs, and ERK1/2 inhibitor could block the IL-17A-elicited activation of DVSMCs.
Conclusions
Our results suggested that IL-17A-derived from patients with SSc might induce the proliferation, collagen synthesis and secretion, and migration of DVSMCs via ERK1/2 signalling pathway, raising the likelihood that IL-17A and ERK1/2 might be promising therapeutic targets for the treatment of SSc-related vasculopathy.